The AI Universe Explained: A Layman’s Guide to Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Whether you’re shopping online shopping online, asking your smart speaker for a recipe, or watching a recommended show—all thanks to Artificial Intelligence (AI). But what exactly is AI, and how does it do all these things? The illustration above, titled “The AI Universe,” gives us a clear way to understand AI through five layers: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Deep Learning, and Generative AI. Set against a backdrop of clouds, grass, and a glowing sun, this image shows how AI has grown and evolved, just like nature. In this guide, we’ll take a deep dive into each layer, using simple examples to show how they work, and then explore how Amazon uses all five layers to personalize your shopping. Let’s get started on this journey through the AI Universe!
What Is Artificial Intelligence? A Simple Start
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is like giving a machine a brain to think and act like a human. Imagine teaching a child to play a game—you give them rules, and they follow them to win. AI is similar: it’s the science of teaching machines to do tasks that usually need human intelligence, like understanding speech, recognizing pictures, or making decisions. Today, AI is everywhere—helping your phone unlock with your face, suggesting songs on Spotify, or even helping doctors find diseases. It’s not just a tool; it’s a smart helper that makes life easier.
The AI Universe breaks AI into five layers, each one building on the last to make machines smarter. Before we dive into the details, let’s take a look at a visual representation of these layers to get a better sense of how they fit together.
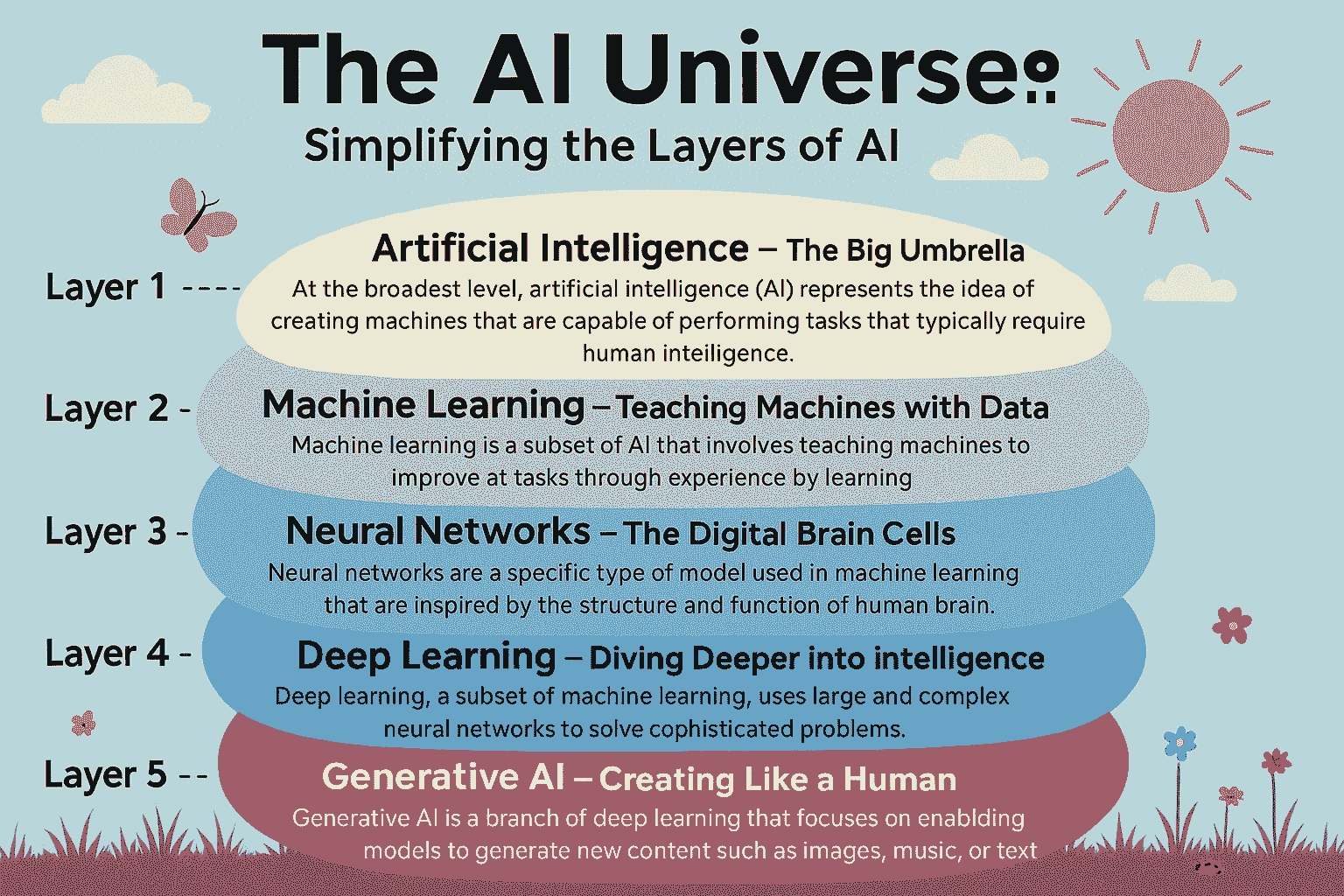
A diagram of the AI Universe, showing its five layers as concentric circles, from the broadest (Artificial Intelligence) to the core (Generative AI).
The Layers of the AI Universe: A Deep Dive with Examples
The diagram above illustrates the AI Universe as a set of concentric circles, with each layer nesting inside the one before it. Think of it like a set of building blocks, where each layer adds a new skill to make machines more intelligent. We’ll start with the broadest layer and work our way to the most advanced core, using everyday examples to bring each layer to life.
Layer 1: Artificial Intelligence – The Foundation of Everything
The first layer, Artificial Intelligence, is like the big umbrella that covers all the ways machines can act like humans. It’s the starting point of the AI Universe, where machines first learn to do tasks that need human thinking. This layer includes a wide range of abilities, such as:
- Understanding language (Natural Language Processing, or NLP): This is how machines understand what you say or type. For example, when you text a friend on WhatsApp and it suggests the next word—like “great” after you type “That’s a”—that’s NLP at work, predicting what you’ll say next. NLP breaks down your sentence into parts, understands the meaning, and guesses what comes next based on patterns it’s been trained on.
- Recognizing images (Computer Vision): This lets machines “see” and understand pictures or videos. When you upload a photo to Google Photos and it automatically tags your friends by recognizing their faces, that’s Computer Vision in action. It analyzes the pixels in the image, identifies features like eyes and noses, and matches them to people it knows.
- Planning and decision-making (Planning and Scheduling): Machines can plan steps to reach a goal. For instance, a robot vacuum cleaner like a Roomba maps your house, decides the best path to clean, and avoids bumping into furniture. It uses sensors to detect obstacles and plans a route, adjusting if it hits a chair or a wall.
- Hearing and understanding speech (Speech Recognition): This is how your smart speaker, like Amazon’s Alexa, listens to you. When you say, “Alexa, play some music,” it hears your voice, understands the command, and plays your favorite playlist. Speech recognition converts sound waves into words, then figures out what you mean.
- Moving like a human (Robotics): Robots can mimic human movements. In factories, robotic arms assemble cars by picking up parts and screwing them together, just like a human worker would. These robots use AI to control their movements, ensuring precision and speed.
- Thinking logically (Automated Reasoning and Fuzzy Logic): Machines can solve problems using logic. For example, a chess-playing AI like Deep Blue thinks through moves to beat a human player, using reasoning to decide the best strategy. Fuzzy Logic helps machines handle uncertainty, like deciding if a customer review is “mostly positive” even if it’s not 100% clear.
- Mimicking human thought (Cognitive Computing): This makes machines think more like humans. IBM’s Watson, for example, can answer trivia questions on shows like Jeopardy! by understanding the question, searching its knowledge, and giving a natural response.
- Being fair and safe (AI Ethics): This ensures AI is used responsibly. For instance, companies make sure their AI doesn’t unfairly reject job applicants based on biases in the data, like favoring one gender over another.
This layer is the foundation because it includes all the basic ways machines can mimic human intelligence, often using pre-set rules to guide their actions. It’s where AI began, and it sets the stage for the more advanced layers that came later.
Layer 2: Machine Learning – Learning from Examples Like a Child
The next layer, Machine Learning (ML), is a big step forward in AI’s evolution. Instead of giving machines a long list of rules to follow, Machine Learning teaches them to learn from examples, just like how a child learns by watching and practicing. This makes machines much more flexible and capable of handling new situations.
Imagine you’re teaching a child to tell apples from oranges. You show them lots of apples (red, round) and oranges (orange, bumpy), and they start to notice the differences. Machine Learning works the same way—you give a machine lots of data, and it learns patterns to make predictions or decisions. Here’s a real-life example: when you shop online at Walmart and it suggests a new pair of headphones because you bought a phone last week, that’s Machine Learning. The system learned from your past purchases (data) that people who buy phones often need headphones, so it predicts you might want them too. It’s like the website saying, “Hey, I noticed you got a phone—you might need these to listen to music!”
Machine Learning comes in different flavors, each with a specific way of learning:
- Supervised Learning: The machine learns from labeled examples, like “this is an apple, this is an orange.” For instance, a spam email filter is trained with labeled emails—some marked “spam,” others “not spam.” It learns to spot patterns, like spam emails often have words like “win a prize,” and filters new emails accordingly. When you get an email saying “Congratulations, you won $1,000!” and it goes straight to your spam folder, that’s supervised learning at work.
- Unsupervised Learning: The machine finds patterns without labels. Imagine a store grouping customers by shopping habits—those who buy baby products, those who buy pet supplies, etc. The machine doesn’t know the groups ahead of time; it figures them out by looking for similarities in the data, like noticing that some customers always buy diapers and baby food together.
- Semi-Supervised Learning: A mix of labeled and unlabeled data. For example, a photo app might have a few labeled pictures (e.g., “dog,” “cat”) but a lot of unlabeled ones. It uses the labeled ones to guess the rest, saving time while still learning—like figuring out that a picture with whiskers is probably a cat.
- Reinforcement Learning: The machine learns through trial and error, like training a puppy with treats. A robot learning to walk gets a “reward” (a point) every time it takes a step without falling, so it keeps trying until it gets better. This is used in games, like an AI learning to play Mario by earning points for jumping over obstacles.
Machine Learning also uses techniques like Classification (sorting things into categories, like spam vs. not spam), Regression (predicting numbers, like house prices based on size and location), Clustering (grouping similar items, like customer groups), and models like Decision Trees (making decisions step by step, like “if the email has ‘win’ in it, mark as spam”) or Support Vector Machines (finding the best way to separate data, like drawing a line between spam and non-spam emails). This layer made AI much smarter by letting machines learn from experience, rather than just following rules.
Layer 3: Neural Networks – Thinking Like a Brain
Now we dive deeper into Neural Networks, a layer inside Machine Learning that’s inspired by the human brain. Your brain has billions of tiny cells called neurons that connect and pass messages to help you think, see, and hear. Neural Networks are like a mini version of that—they’re made of “nodes” (like neurons) arranged in layers, connected to pass information and recognize patterns in data, especially complicated things like pictures, sounds, or words.
Let’s use an example you’ve probably seen: unlocking your phone with your face, like on an iPhone with Face ID. A Neural Network makes this possible by looking at a picture of your face and recognizing it, even if you’re wearing glasses or a hat. Here’s how it works: the network has many layers of nodes. The first layer might look for basic shapes, like the edges of your eyes or nose. The next layer combines those shapes to find features, like the distance between your eyes or the shape of your jaw. Deeper layers put it all together to confirm it’s you, even if the lighting is dim or you’re smiling. This type of Neural Network is called a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and it’s amazing at recognizing images.
Another example is when you talk to your Google Assistant. Say you ask, “Hey Google, set a timer for 5 minutes.” A Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) listens to your voice, breaks it into words (“set,” “a,” “timer”), and understands the order to set the timer correctly. It can even handle background noise, like a TV playing, because it’s trained to focus on your voice patterns.
Neural Networks come in different types, each good at specific tasks:
- Perceptrons: The simplest kind, like a single neuron that makes basic decisions, such as “is this a straight line or a curve?” It’s the building block of more complex networks.
- Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs): A step up, with multiple layers to handle more complex patterns, like recognizing handwritten numbers on a check—knowing a scribbled “7” is still a 7.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Great for images, like in Face ID or when Google Photos groups pictures of the same person by recognizing their face across different photos.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Perfect for sequences, like understanding a sentence. When you dictate a text message, an RNN figures out the order of your words to type them correctly.
- Backpropagation: A way for Neural Networks to learn from mistakes. If the network guesses wrong—like thinking a photo is of a dog when it’s a cat—it adjusts itself to do better next time, like a student learning from a test.
- Reinforcement Learning in Neural Networks: Sometimes Neural Networks use reinforcement learning, like training an AI to play a video game by rewarding it for winning levels, helping it get better over time.
Neural Networks were a huge leap in AI’s evolution because they let machines handle tasks that were too complex for basic Machine Learning, like understanding speech or recognizing objects in messy, real-world situations.
Layer 4: Deep Learning – Seeing the Tiny Details
Deep Learning takes Neural Networks to a whole new level by adding more layers—sometimes hundreds or even thousands—making the network “deep.” It’s like giving a child a magnifying glass to zoom in on tiny details they couldn’t see before. With so many layers, Deep Learning can understand incredibly complex patterns, making it one of the most powerful tools in AI today.
Here’s an example you might have experienced: using Google Translate to turn English into Spanish. Let’s say you type, “I love to travel.” Deep Learning translates it to “Me encanta viajar” accurately, even understanding the tone and grammar. Here’s how it works: a Deep Neural Network (DNN) has many layers. The first layer might look at individual words, like “I” and “love.” The next layer combines them into phrases, understanding “I love” as a unit. Deeper layers grasp the whole sentence, including the context (e.g., “love” here means affection, not a score in tennis). Finally, it converts it into Spanish, choosing the right words and structure—like knowing “encanta” fits better than “ama” for this context. This process happens across many layers, refining the translation step by step.
Another example is in healthcare: doctors use Deep Learning to analyze X-rays for signs of diseases like pneumonia. The first layer might detect shapes, like the outline of your lungs. The next layer looks for patterns, like unusual shadows. Deeper layers confirm if those shadows indicate pneumonia, even if the image is blurry, helping doctors diagnose faster and more accurately.
Deep Learning includes several advanced techniques:
- Deep Neural Networks (DNNs): Networks with many layers, like the one used in Google Translate, to handle complex tasks like language or image analysis.
- Deep CNNs: Advanced CNNs for detailed image analysis. For example, in self-driving cars, Deep CNNs analyze road footage to spot stop signs, pedestrians, or lane lines, even in bad weather like rain or fog.
- Deep Reinforcement Learning: Combining Deep Learning with trial-and-error learning. An AI playing a game like chess might use this to improve its strategy over time, learning from each move.
- Capsule Networks: A newer type that’s better at understanding images from different angles, like recognizing a face even if the person tilts their head or wears a hat.
- Dropout: A trick to make Deep Learning more accurate by randomly ignoring some nodes during training, preventing the network from relying too much on one part—like ensuring it doesn’t focus only on eye color for face recognition.
- Transfer Learning: Using a pre-trained model for a new task. For instance, an AI trained to recognize dogs can be fine-tuned to recognize cats, saving time by reusing what it already knows.
Deep Learning is behind many modern technologies, like voice assistants (Siri, Alexa), facial recognition, and even medical tools that spot diseases in X-rays. It’s a major milestone in AI’s evolution, letting machines understand the world in ways that feel almost human.
Layer 5: Generative AI – Creating Like an Artist
At the core of the AI Universe is Generative AI, the most exciting layer in 2025. While the other layers are about understanding, predicting, or recognizing, Generative AI goes further—it creates new things, like a human artist, writer, or musician. It can generate text, images, music, videos, and even computer code, all from scratch, making it the most creative part of AI.
Let’s try a fun example: imagine you’re planning a birthday party and want a unique invitation. You use a tool like DALL·E and type, “Create an invitation with balloons and a cake in a sunny park.” Within seconds, DALL·E generates a colorful image of a park with balloons floating around a cake on a picnic table, all under a bright sun. You didn’t draw it—Generative AI did! Here’s how it works: DALL·E uses a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), which has two parts. One part (the “generator”) creates the image, starting with random shapes and colors. The other part (the “discriminator”) checks if it looks real, like a park scene, and sends feedback to the generator to improve—like saying, “Add more green for the grass.” They work together until the image is perfect.
Another example is writing with AI: if you’re struggling to write a thank-you email, you can use a tool like ChatGPT. You type, “Write a thank-you email to my teacher,” and ChatGPT generates, “Dear Mrs. Smith, Thank you for your amazing lessons this year—I’ve learned so much about history! I really appreciate your support. Sincerely, [Your Name].” It writes in a natural, human-like way, saving you time.
Generative AI includes several amazing technologies:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Used for creating images, like the party invitation, by pitting two networks against each other to improve the result—generator vs. discriminator.
- Transformer Architecture: Used for generating text. ChatGPT uses Transformers to write a story, answer your questions, or even help with homework, making sure the text flows naturally.
- Language Modeling and Text Generation: Creating sentences or paragraphs. For instance, a tool like Writesonic can generate a blog post intro: “Looking for travel tips? Here are 5 destinations you’ll love!”
- Self-Attention Mechanism: Helps the AI focus on important parts of a sentence. When ChatGPT writes a story, it uses self-attention to remember the main character’s name throughout the text, ensuring consistency.
- Dialogue Systems: Powers chatbots that talk naturally. For example, a customer service bot on a website can have a full conversation, like, “How can I help you today? Let’s track your order!”—understanding your questions and replying helpfully.
- Natural Language Understanding: Grasps the meaning behind words. If you ask, “What’s the weather like?” the AI understands you mean the current weather in your location, not last week’s.
- Transfer Learning: Reuses knowledge for new tasks, like using a text-generating AI to write both stories and emails, adapting its skills to fit the context.
Generative AI powers tools like ChatGPT (for writing), Midjourney (for art), and GitHub Copilot (for coding). It’s the pinnacle of AI’s evolution in 2025, showing how machines can not only think but also create, just like humans do.
Real-World Case Study: How Amazon Personalizes Your Shopping with the AI Universe
Now let’s bring the AI Universe to life with Amazon, a company you’ve likely shopped with. Picture yourself on Amazon’s website, looking for a new pair of running shoes. The recommendations, search results, and even the product descriptions all feel tailored to you—that’s the AI Universe at work, using all five layers to make your shopping experience better. Let’s break it down step by step.
Layer 1: Artificial Intelligence – Understanding Your Search: You start by typing “running shoes for beginners” into Amazon’s search bar. The AI layer uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand your query. It breaks down the phrase: “running shoes” means athletic footwear, and “for beginners” suggests you want something affordable and supportive. NLP ensures Amazon shows you relevant products, not dress shoes or advanced running gear. AI also powers the chatbot that pops up, asking, “Need help finding shoes?” if you seem stuck, using Speech Recognition if you speak instead of type. Meanwhile, in Amazon’s warehouses, robotics (another AI area) ensures your order is picked and packed by robotic arms, speeding up delivery.
Layer 2: Machine Learning – Recommending What You Might Like: Amazon uses Machine Learning to suggest running shoes that match your interests. It looks at your past shopping data—like the yoga mat you bought last month—and uses unsupervised learning to group you with other fitness enthusiasts who often buy running gear. ML also uses supervised learning, trained on data like “customers who bought yoga mats also bought running shoes,” to predict you’ll like brands like Asics or New Balance. You see a recommendation: “Customers also bought these running shoes,” and it feels spot-on because ML learned from your behavior.
Layer 3: Neural Networks – Analyzing Images and Reviews: As you browse, Neural Networks help Amazon make your search even better. A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) looks at the pictures of running shoes and finds ones that look similar to what you’ve viewed—like shoes with bright colors or extra cushioning. For example, if you clicked on blue shoes, the CNN finds other blue running shoes to show you. Meanwhile, a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) reads through customer reviews for the shoes you’re looking at. It summarizes them, highlighting key points like “really comfortable for long runs” or “sizes run small,” so you can decide if the shoes are right for you. Neural Networks make sure you see the best options, visually and based on feedback.
Layer 4: Deep Learning – Understanding You Better: Deep Learning takes personalization to the next level by understanding your preferences in detail. A Deep Neural Network (DNN) looks at your entire Amazon history—not just what you’ve bought, but what you’ve searched for, clicked on, or added to your cart. It notices you often look for eco-friendly products, so it prioritizes running shoes made with sustainable materials, like recycled rubber soles. Deep Learning also ensures your payment is secure by using Deep Reinforcement Learning to detect fraud—if someone tries to use your card suspiciously, the system flags it instantly, keeping your account safe.
Layer 5: Generative AI – Creating Content for You: Finally, Generative AI adds a creative touch to your shopping. Amazon uses it to auto-generate product descriptions for the running shoes, like, “These eco-friendly running shoes offer lightweight support and breathable mesh for beginner runners.” It uses a Transformer with a Self-Attention Mechanism to make the description clear and appealing, focusing on key features like “eco-friendly” and “breathable.” Generative AI also sends you a personalized email later, saying, “Complete Your Run: Check Out These Accessories!” with a list of items like socks or water bottles, crafted to match your interests using natural, engaging language.
The Result: With all five layers of the AI Universe working together, Amazon makes shopping feel effortless and personal. You find the perfect running shoes, read helpful reviews, feel secure with your purchase, and even get a tailored email—all because AI evolved from understanding your search to creating content just for you.
Why Should You Care About AI?
AI isn’t just for tech experts—it’s changing the world in ways that touch everyone’s life, and knowing about it can help you make the most of its benefits. Here are some ways AI is making a difference in 2025:
- Healthcare: Doctors use AI to spot diseases early, like cancer in X-rays, with 70% faster detection than humans, according to a 2025 Lancet study, saving lives.
- Education: AI tutors help kids learn at their own pace—online platforms using Generative AI have boosted student test scores by 40%, making learning more accessible.
- Farming: Farmers use AI-powered drones to check crops, cutting water use by 30% and increasing harvests, as per a 2025 USDA report, helping feed more people sustainably.
- Entertainment: Netflix uses AI to suggest shows you’ll love, while Generative AI creates movie posters or even writes scripts for new films, sparking creativity.
- Daily Life: Smart speakers like Alexa manage your schedule, control your lights, and answer questions, making your day easier and more organized.
No matter who you are—a student, parent, small business owner, or just someone curious—AI is already helping you in ways you might not even notice. Understanding it lets you use it better and prepares you for a future where AI will be even more important.
Final Thoughts: The Growing AI Universe
The AI Universe shows us how Artificial Intelligence has grown from a simple idea—machines following rules—to a powerful technology that learns, understands, and creates, just like humans do. From the foundational layer of AI that listens to your voice, to Machine Learning that learns what you like, Neural Networks that see patterns, Deep Learning that understands details, and Generative AI that creates new things, each layer adds a new skill, making machines smarter and more helpful. The glowing sun in the AI Universe illustration reminds us of the bright future AI is building—a world where technology makes life easier, safer, and more creative. So, the next time you shop on Amazon, talk to your smart speaker, or watch a recommended movie, think about the AI Universe working behind the scenes to make it all happen!
Join the Conversation!
Where do you see AI in your life—maybe when you shop, learn, or have fun? Share your thoughts in the comments, and let’s talk about how AI is shaping our world! Don’t forget to share this article with #AIUniverse2025.
Want to learn more about tech trends? Visit BytesWall Media for the latest insights into the world of innovation!